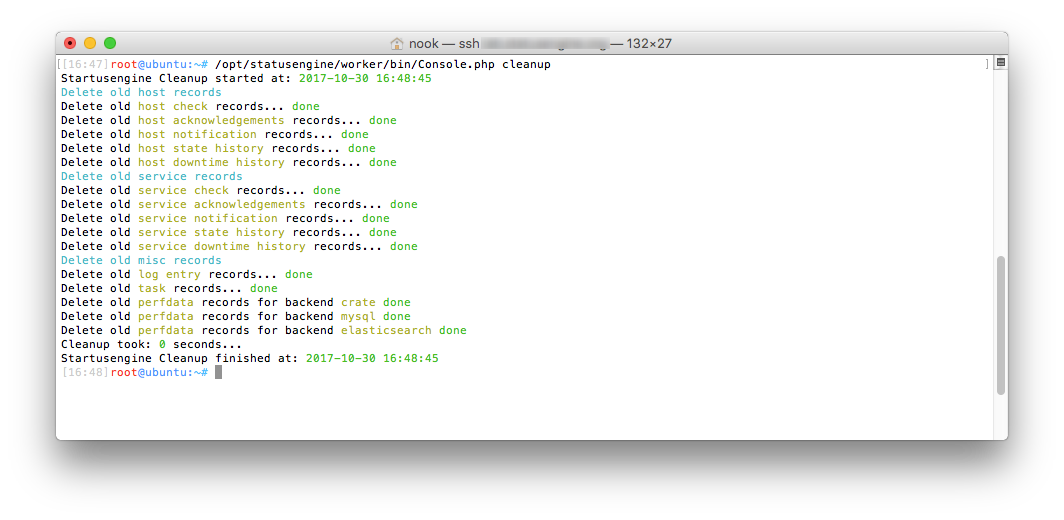
Store Nagios or Naemon Performance Data to MySQL
In this tutorial, we are going to configure your system, to store Nagios and Naemon Performance Data into an MySQL database.
In addition, I will show you, how to use this data via Statusengine UI and Grafana.
All commands needs to run as user root or via sudo.
Requirements
MySQL Server - If you don't have MySQL installed yet - follow this guide.
Nagios or Naemon with loaded Statusengine Broker Module
Running Statusengine Worker
Recommended
Configure Statusengine Broker Module to export performance data
If not already done, add use_service_perfdata=1 to your Statusengine Broker Module options
and restart your Nagios or Naemon process.
Configure Statusengine Worker to store performance data to MySQL
Open the file /opt/statusengine/worker/etc/config.yml to adjust the following values
# If Statusengine should save historical data to MySQL
# WARNING: Do not set use_mysql and use_crate to 1 at the same time!
use_mysql: 0
# Configuration of your MySQL server
mysql:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 3306
username: statusengine
password: password
database: statusengine
############
# PERFDATA DATA CONFIGURATION
############
# If statusengine should process performance data or not
# 1 = yes
# 0 = no
process_perfdata: 1
# Number of worker processes for service check results
# Target: You selected this at 'perfdata_backend' option
number_perfdata_worker: 1
# Uncomment to enable
# You can enable as much backends as you want
perfdata_backend:
# - crate
# - graphite
# - elasticsearch
- mysql
Even if you set use_mysql=0, because you don't want to use MySQL as Storage Backend for your status data, you can still use it to
store your performance data into it.
The metrics will be exported to the table statusengine_perfdata.
To load the new configuration, you need to restart Statusengine Worker.
systemctl restart statusengine.service
PS: You can enable multiple performance data backends if you want.
Example:
perfdata_backend:
- crate
- graphite
- mysql
- elasticsearch
Check Table for Performance Data records
After you restared Statusengine Worker, you should query your database to make sure, that performance data records gets saved to your database.
mysql> use statusengine
Database changed
mysql> SELECT COUNT(*) FROM statusengine_perfdata;
+----------+
| COUNT(*) |
+----------+
| 2666 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
mysql>
The amount of records you will see, depends on how many checks your system executes and how frequently they get executed.
If your result is zero, you should wait a few minutes before you continue with this guide.
Configure Statusengine Ui
Statusengine Ui is able to render basic performance data, from an MySQL data source.
Open the file /usr/share/statusengine-ui/etc/config.yml to adjust the following values
# If Statusengine Ui should load status data from MySQL
# WARNING: Do not set use_mysql and use_crate to 1 at the same time!
use_mysql: 0
# Configuration of your MySQL server
mysql:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 3306
username: statusengine
password: password
database: statusengine
############
# PERFDATA DATA CONFIGURATION
############
# Determine if the Statusengine Ui should use on of the following
# perfdata_backend's to load and display performance data
# 0 disable, 1 enable
display_perfdata: 1
# Uncomment to enable
# CrateDB as Performance Data Backend
# CrateDB is the default at the moment
#perfdata_backend: crate
# Graphite as Performance Data Backend
#perfdata_backend: graphite
# MySQL as Performance Data Backend
perfdata_backend: mysql
# Elasticsearch as Performance Data Backend
#perfdata_backend: elasticsearch
Important! Only one perfdata_backend could be enabled at the same time!
Even if you set use_mysql=0, because you don't want to use MySQL as Storage Backend for your status data, you can still use it to query your performance data.
Configure Grafana
Once performance data gets stored to MySQL, you can also use Grafana to build up own dashboards.
Add MySQL data source
Build your first dashboard
Every query will follow this schema:
SELECT
timestamp_unix as time_sec,
value,
label as metric
FROM statusengine_perfdata
WHERE timestamp_unix > $__unixEpochFrom()
AND timestamp_unix < $__unixEpochTo()
AND hostname="$HOSTADDRESS$"
AND service_description="$SERVICEDESCRIPTION$"
AND label="$METRIC$"
ORDER BY timestamp_unix ASC
Example:
SELECT
timestamp_unix as time_sec,
value,
label as metric
FROM statusengine_perfdata
WHERE timestamp_unix > $__unixEpochFrom()
AND timestamp_unix < $__unixEpochTo()
AND hostname="localhost"
AND service_description="Total Processes"
AND label="procs"
ORDER BY timestamp_unix ASC
The Macros $__unixEpochFrom() and $__unixEpochTo() will be replaced by Grafana automatically.
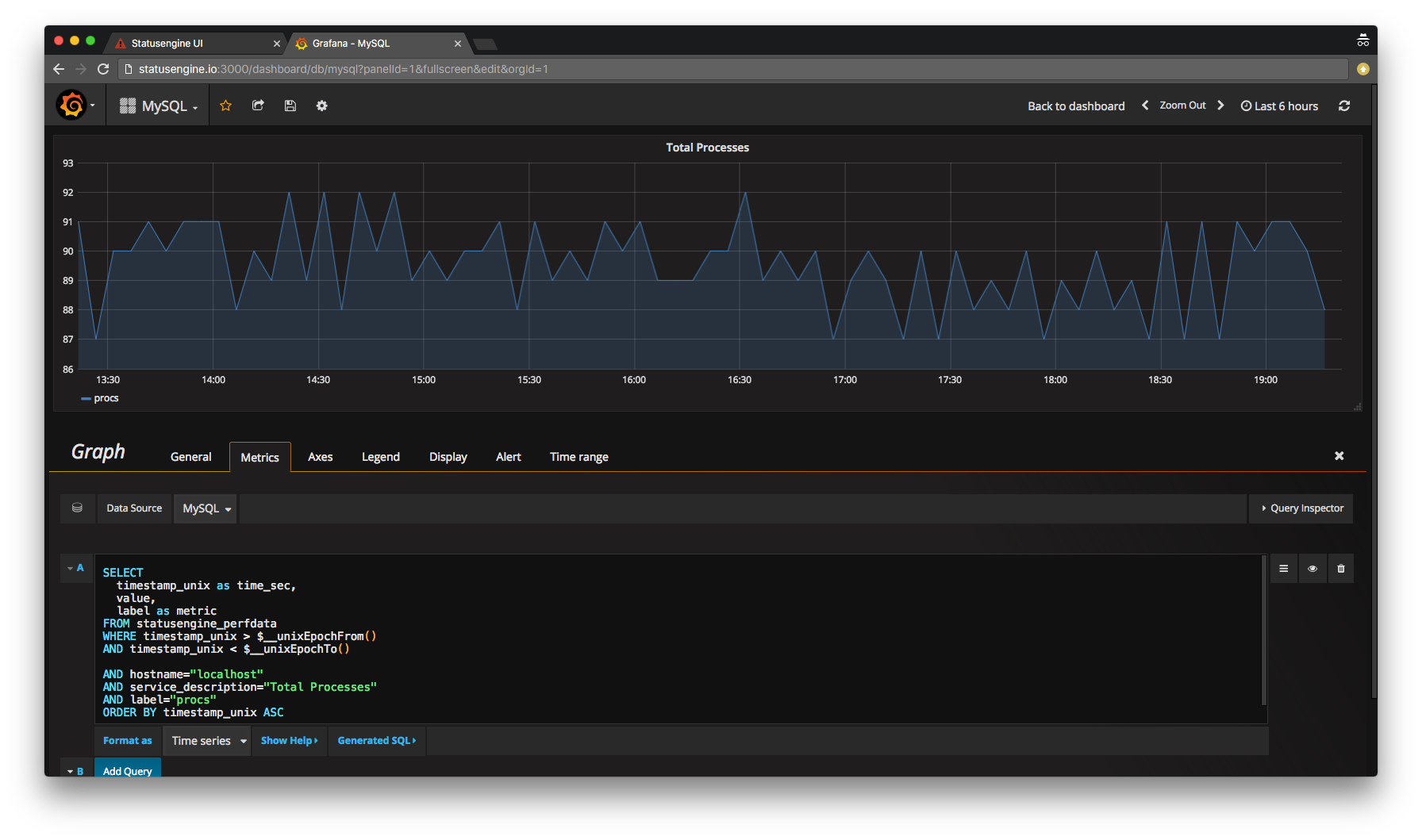
Make sure, that you set Display Null value connected
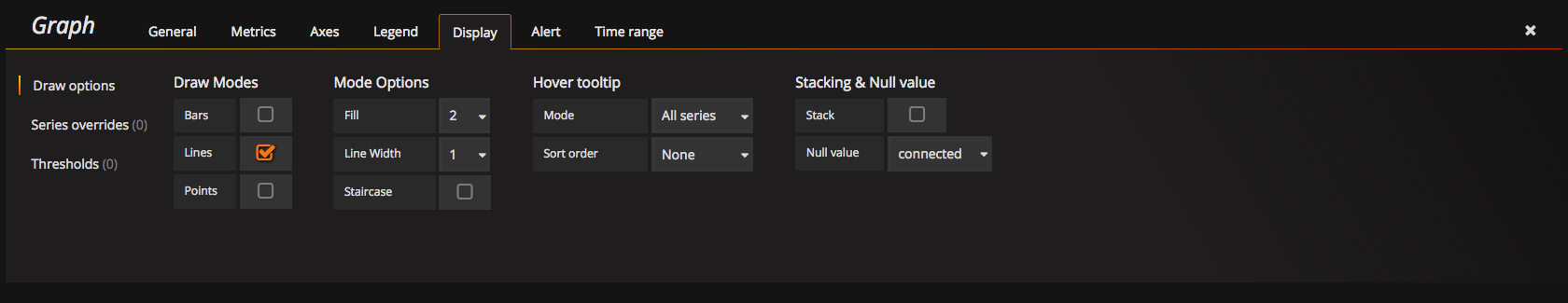
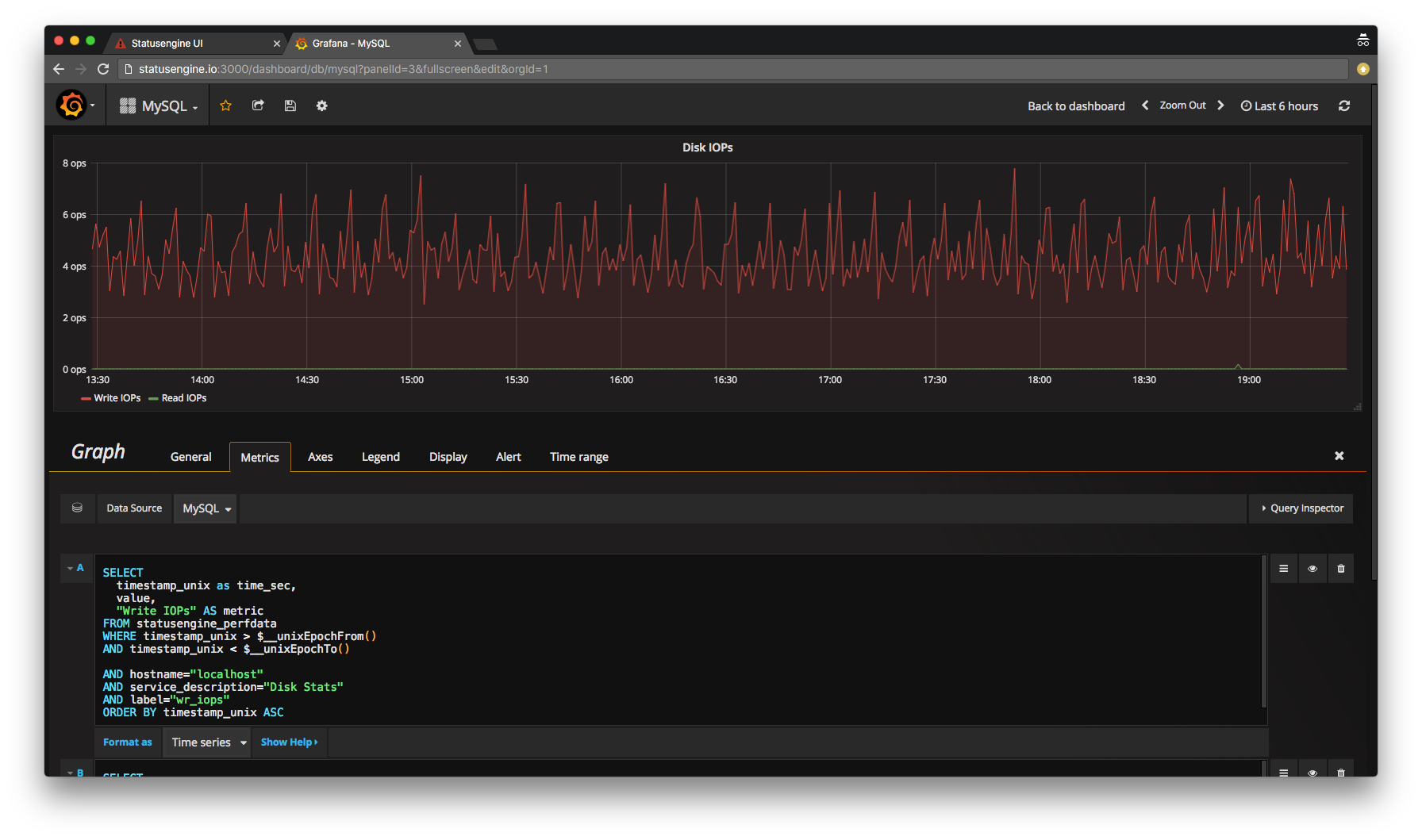
You can also create an alias for your Metric names
SELECT
timestamp_unix as time_sec,
value,
"Write IOPs" AS metric
FROM statusengine_perfdata
WHERE timestamp_unix > $__unixEpochFrom()
AND timestamp_unix < $__unixEpochTo()
AND hostname="localhost"
AND service_description="Disk Stats"
AND label="wr_iops"
ORDER BY timestamp_unix ASC
Play around
Deletion of old records
The MySQL Performance Data implementation is very simple. There are no partitions in use and data will just save as in every other table you know.
mysql> SELECT * FROM statusengine_perfdata LIMIT 10;
+-----------+---------------------+--------+---------------+----------------+----------+------+
| hostname | service_description | label | timestamp | timestamp_unix | value | unit |
+-----------+---------------------+--------+---------------+----------------+----------+------+
| localhost | Current Users | users | 1508781382000 | 1508781382 | 3 | NULL |
| localhost | PING | rta | 1508781446000 | 1508781446 | 0.044 | ms |
| localhost | PING | pl | 1508781446000 | 1508781446 | 0 | % |
| localhost | Root Partition | / | 1508781501000 | 1508781501 | 3561 | MB |
| localhost | Current Load | load1 | 1508781519000 | 1508781519 | 0.16 | NULL |
| localhost | Current Load | load5 | 1508781519000 | 1508781519 | 0.24 | NULL |
| localhost | Current Load | load15 | 1508781519000 | 1508781519 | 0.17 | NULL |
| localhost | Swap Usage | swap | 1508781549000 | 1508781549 | 24573 | MB |
| localhost | SSH | time | 1508781569000 | 1508781569 | 0.009121 | s |
| localhost | Total Processes | procs | 1508781614000 | 1508781614 | 76 | NULL |
+-----------+---------------------+--------+---------------+----------------+----------+------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
The Statusengine Cleanup Cronjob will delete every record, where timestamp_unix is less than age_perfdata. age_perfdata is set in days.